Search for matlab, proteus, arduino, Engineering & Architecture freelancers. Refine your freelance experts search by skill, location and price. Check freelancers\'. Serial Communication (1) Signal Coding (10) SIL (1) Simulations (13) Sin Wave (4) SISO (1) SLAM (1) SoC (2) Solar Inverter Control with Simulink (3) Sound (4. This video explains how to program arduino board using simulink. In this video, Arduino uno is programmed using simulink MATLAB and also. Bisection Method for Solving non-linear.
Use Serial Communications with Arduino Hardware
Arduino® hardware has serial ports, also known as UARTs,that can communicate with other devices that have serial interfaces.
Hardware
You can use serial port 0 to communicate with other devicesthat have serial ports, or to communicate with a computer over theUSB port. Each serial port supports one Serial Transmit and one SerialReceive block, one block per pin. You can run your model in the Externalmode for all the Arduino boards.To know pin mapping for different Arduino boards,see Pin Mapping Table in: Pin Mapping on Arduino Blocks.
Warning
Do not connect the serial port pins to an RS-232 serial interface,such as the DE-9M connector on a computer, without limiting the voltage.The RS-232 standard allows higher voltages that can damage your hardware.For details, read the documentation for your Arduino hardware.
Transmit Serial Data
To transmit data through a serial port or USB port on the Arduinohardware:
Add the Serial Transmit block to your model.
Connect a data source to the block input on the SerialTransmit block.
If the data type is not uint8, use a Data Type Conversion blockto convert it to uint8.
In the Arduino Serial Transmit block,select a Port number.
Click the Tools menu in the model, and select Run on Target HardwareOptions.
In the Configuration Parameters dialog that opens, on the HardwareImplementation > Serial port properties, set the baud rate forthe serial port you selected in the Arduino Serial Transmit block.
Connect the appropriate digital transmit pin to thehardware that receives the data.
Run the model, as described in Run Model on Arduino Hardware.
If your model uses the Arduino USB port (Serialport 0) to transmit data to a device that is not your host computer,reconnect the USB cable to that device and press the RESET button.
Receive Serial Data
To receive data through a serial port or USB port on the Arduino hardware:
Add the Serial Receive block to your model.
On the Arduino Serial Receive block,connect the Data block output to a block thatuses the data.
Open the Arduino Serial Receive blockand specify the Port number.
Click the Tools menu inthe model, and select Run on Target Hardware > Options.
In the Configuration Parameters dialog that opens, on the HardwareImplementation > Serial port properties, set the baud rate forthe serial port you selected in the Arduino Serial Receive block.
Connect the digital receive pin to the hardware thattransmits the data.
Run the model, as described in Run Model on Arduino Hardware.
If your model uses the Arduino USB port (Serialport 0) to receive data from a device that is not your host computer,reconnect the USB cable to that device and press the RESET button.
Related Topics
Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware
This example shows how to use Simulink® Support Package for Arduino® Hardware to send and receive serial data with Arduino hardware.
Supported Hardware
Arduino Mega 2560
Arduino Mega ADK
Arduino Uno
Arduino Due
Arduino MKR1000
Arduino MKR WIFI 1010
Arduino ZERO
Arduino Leonardo
Introduction
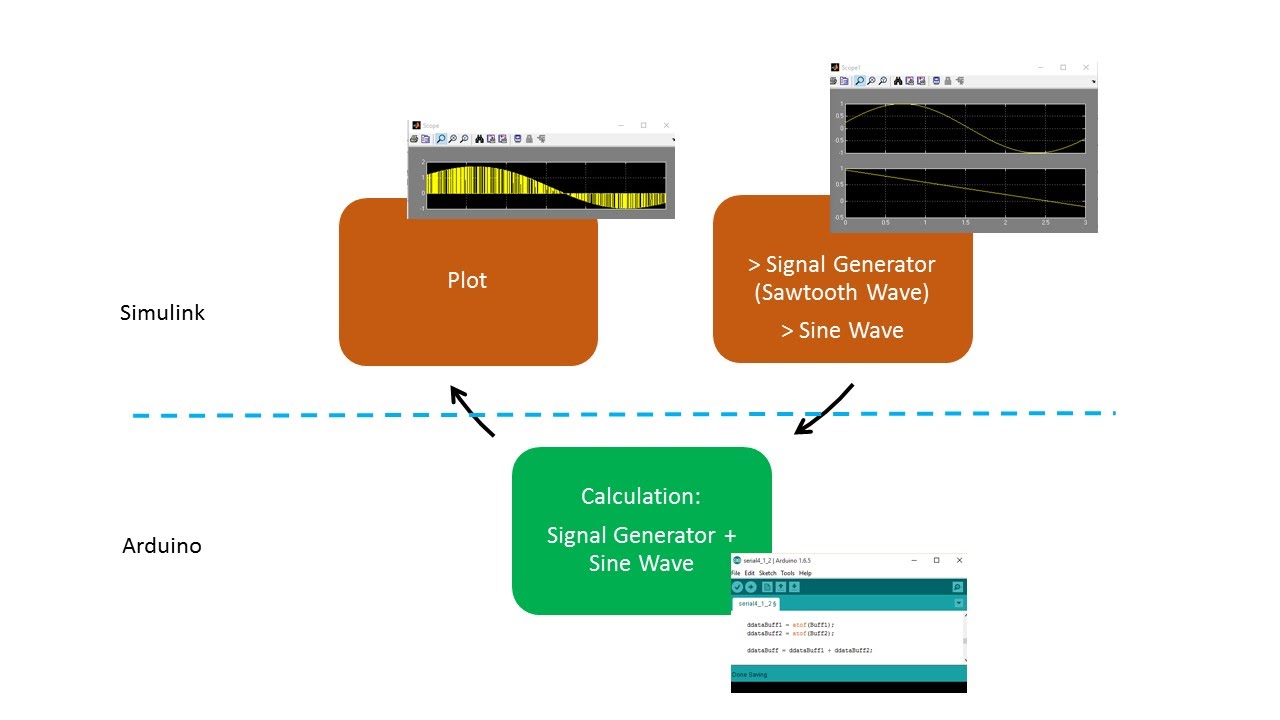
In this example, the Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware and Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware models are used to send and receive serial data. These models use the Serial Transmit and Serial Receive blocks to exchange data.
Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware: In this model, the TX1 pin sends serial data to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. This model is configured to run in External mode. For more information on External mode, see Tune and Monitor Model Running on Arduino Hardware.
Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware: In this model, the Arduino hardware sends data to your computer over the serial port 0 (USB port) of the Arduino hardware. This model is configured to run in Normal mode. In this mode, the model is deployed on the Arduino hardware.
The models provided in this example are preconfigured for the Arduino Mega 2560 board. You can run these models on any of the boards listed in the Supported Hardware section by changing the Hardware board parameter in the Simulink model. For more information on how to change the Hardware board parameter, see the Step 2: Configure the Model for Arduino Hardware section of this example.
Prerequisites
Before you start with this example, we recommend you complete the following:
Getting Started with Arduino Hardware example
Communicating with Arduino Hardware example
Required Hardware
To run this example, you must have the following hardware:
Step 1: Connect TX and RX Pins on Arduino Hardware
1. Connect your Arduino board to your computer using the USB cable.
2. Connect the TX1 pin to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. This connection is a loopback connection.
Step 2: Configure the Model for Arduino Hardware
1. Open the Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware model. This model is configured to run in External mode.
2. To configure the model, click the Model Configuration Parameters button on the Simulink toolbar.
3. In the Configurations Parameters dialog box, select Hardware Implementation.
4. From the Hardware board list, select the type of Arduino board that you are using.
5. From the Groups list under Target hardware resources, select Serial port properties.
The Serial 1 baud rate parameter is set to 9600. In this example, the baud rate of Serial 1 baud rate is set because the TX1 and RX1 pins correspond to the Serial port 1 of the Arduino hardware. If you are using any other serial port pins for communication, specify the baud rate of the corresponding serial port.

6. Click Apply. Click OK to close the dialog box.
Step 3: Configure the Blocks in the Simulink Model
Double-click these blocks and verify the parameter values specified in the Block Parameters dialog box.
Note:
Because the TX1 pin is connected to the RX1 pin, specify the Serial Port parameter of the
Serial Transmitblock and the Port number parameter of theSerial Receiveblock as1.The Sample time parameter specified in the
Constantblock and theSerial Receiveblock must be the same.
Step 4: Run the Model in External Mode
1. On the model toolbar, set Simulation mode to External.
2. The default Simulation stop time is 10.0 seconds. To run the model for an indefinite period, enter inf.
3. Click Run. The lower left corner of the model window displays status while Simulink prepares, downloads, and runs the model on the hardware.
At each time step, the TX1 pin transmits the data specified in the Constant block to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. The RX1 pin receives the data and displays it on the Display Output block.
4. Observe the output in the Display Output and Display Status blocks.
5. Disconnect the wire from the RX1 pin. Both the Display blocks now output 0. A value of 0 in the Display Status block indicates that no data is received at the given time step. If you reconnect the wire again, you can see that the values at the Display blocks are restored.
6. To stop running the model on your hardware, click Stop on the model toolbar.
Step 5: Run the Model in Normal Mode
1. Remove the wire connecting RX1 and TX1 pins because in this model, the data is sent to a serial terminal over the Serial port 0 (USB port).
2. Open the Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware model. This model is configured to run in Normal mode.
3. In the Configurations Parameters dialog box, go to Hardware Implementation > Target hardware resources > Groups > Serial port properties. Set Serial 0 baud rate to the maximum baud rate supported by the serial port of your Arduino hardware.
4. Double-click the Serial Transmit block and verify these parameter values.
5. On the model toolbar, set Simulation mode to Normal and click the Deploy to Hardware button. The lower left corner of the model window displays status while Simulink prepares, downloads, and runs the model on the hardware.
6. Open the serial terminal in your computer ( for example, Arduino IDE serial monitor). When logging in to the serial terminal:
Specify the COM port number that corresponds to your serial connection. To learn how to find the COM port number, see Configure Host COM Port.
Specify the baud rate to the same value as the baud rate set in the Model Configuration Parameters dialog box. In this example, the baud rate is
115200.
Garena free fire online play. After you login to the serial terminal, you can see that the counter values are displayed with label Counter_val :.
Other Things to Try
Configure Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware model to exchange data over other serial ports of the Arduino hardware.
Create a Simulink model that uses
Serial ReceiveandSerial Sendblocks from Instrument Control Toolbox to exchange serial data between your computer and Arduino hardware.
Search for matlab, proteus, arduino, Engineering & Architecture freelancers. Refine your freelance experts search by skill, location and price. Check freelancers\'. Serial Communication (1) Signal Coding (10) SIL (1) Simulations (13) Sin Wave (4) SISO (1) SLAM (1) SoC (2) Solar Inverter Control with Simulink (3) Sound (4. This video explains how to program arduino board using simulink. In this video, Arduino uno is programmed using simulink MATLAB and also. Bisection Method for Solving non-linear.
Use Serial Communications with Arduino Hardware
Arduino® hardware has serial ports, also known as UARTs,that can communicate with other devices that have serial interfaces.
Hardware
You can use serial port 0 to communicate with other devicesthat have serial ports, or to communicate with a computer over theUSB port. Each serial port supports one Serial Transmit and one SerialReceive block, one block per pin. You can run your model in the Externalmode for all the Arduino boards.To know pin mapping for different Arduino boards,see Pin Mapping Table in: Pin Mapping on Arduino Blocks.
Warning
Do not connect the serial port pins to an RS-232 serial interface,such as the DE-9M connector on a computer, without limiting the voltage.The RS-232 standard allows higher voltages that can damage your hardware.For details, read the documentation for your Arduino hardware.
Transmit Serial Data
To transmit data through a serial port or USB port on the Arduinohardware:
Add the Serial Transmit block to your model.
Connect a data source to the block input on the SerialTransmit block.
If the data type is not uint8, use a Data Type Conversion blockto convert it to uint8.
In the Arduino Serial Transmit block,select a Port number.
Click the Tools menu in the model, and select Run on Target HardwareOptions.
In the Configuration Parameters dialog that opens, on the HardwareImplementation > Serial port properties, set the baud rate forthe serial port you selected in the Arduino Serial Transmit block.
Connect the appropriate digital transmit pin to thehardware that receives the data.
Run the model, as described in Run Model on Arduino Hardware.
If your model uses the Arduino USB port (Serialport 0) to transmit data to a device that is not your host computer,reconnect the USB cable to that device and press the RESET button.
Receive Serial Data
To receive data through a serial port or USB port on the Arduino hardware:
Add the Serial Receive block to your model.
On the Arduino Serial Receive block,connect the Data block output to a block thatuses the data.
Open the Arduino Serial Receive blockand specify the Port number.
Click the Tools menu inthe model, and select Run on Target Hardware > Options.
In the Configuration Parameters dialog that opens, on the HardwareImplementation > Serial port properties, set the baud rate forthe serial port you selected in the Arduino Serial Receive block.
Connect the digital receive pin to the hardware thattransmits the data.
Run the model, as described in Run Model on Arduino Hardware.
If your model uses the Arduino USB port (Serialport 0) to receive data from a device that is not your host computer,reconnect the USB cable to that device and press the RESET button.
Related Topics
Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware
This example shows how to use Simulink® Support Package for Arduino® Hardware to send and receive serial data with Arduino hardware.
Supported Hardware
Arduino Mega 2560
Arduino Mega ADK
Arduino Uno
Arduino Due
Arduino MKR1000
Arduino MKR WIFI 1010
Arduino ZERO
Arduino Leonardo
Introduction
In this example, the Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware and Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware models are used to send and receive serial data. These models use the Serial Transmit and Serial Receive blocks to exchange data.
Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware: In this model, the TX1 pin sends serial data to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. This model is configured to run in External mode. For more information on External mode, see Tune and Monitor Model Running on Arduino Hardware.
Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware: In this model, the Arduino hardware sends data to your computer over the serial port 0 (USB port) of the Arduino hardware. This model is configured to run in Normal mode. In this mode, the model is deployed on the Arduino hardware.
The models provided in this example are preconfigured for the Arduino Mega 2560 board. You can run these models on any of the boards listed in the Supported Hardware section by changing the Hardware board parameter in the Simulink model. For more information on how to change the Hardware board parameter, see the Step 2: Configure the Model for Arduino Hardware section of this example.
Prerequisites
Before you start with this example, we recommend you complete the following:
Getting Started with Arduino Hardware example
Communicating with Arduino Hardware example
Required Hardware
To run this example, you must have the following hardware:
Step 1: Connect TX and RX Pins on Arduino Hardware
1. Connect your Arduino board to your computer using the USB cable.
2. Connect the TX1 pin to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. This connection is a loopback connection.
Step 2: Configure the Model for Arduino Hardware
1. Open the Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware model. This model is configured to run in External mode.
2. To configure the model, click the Model Configuration Parameters button on the Simulink toolbar.
3. In the Configurations Parameters dialog box, select Hardware Implementation.
4. From the Hardware board list, select the type of Arduino board that you are using.
5. From the Groups list under Target hardware resources, select Serial port properties.
The Serial 1 baud rate parameter is set to 9600. In this example, the baud rate of Serial 1 baud rate is set because the TX1 and RX1 pins correspond to the Serial port 1 of the Arduino hardware. If you are using any other serial port pins for communication, specify the baud rate of the corresponding serial port.

6. Click Apply. Click OK to close the dialog box.
Step 3: Configure the Blocks in the Simulink Model
Double-click these blocks and verify the parameter values specified in the Block Parameters dialog box.
Note:
Because the TX1 pin is connected to the RX1 pin, specify the Serial Port parameter of the
Serial Transmitblock and the Port number parameter of theSerial Receiveblock as1.The Sample time parameter specified in the
Constantblock and theSerial Receiveblock must be the same.
Step 4: Run the Model in External Mode
1. On the model toolbar, set Simulation mode to External.
2. The default Simulation stop time is 10.0 seconds. To run the model for an indefinite period, enter inf.
3. Click Run. The lower left corner of the model window displays status while Simulink prepares, downloads, and runs the model on the hardware.
At each time step, the TX1 pin transmits the data specified in the Constant block to the RX1 pin of your Arduino hardware. The RX1 pin receives the data and displays it on the Display Output block.
4. Observe the output in the Display Output and Display Status blocks.
5. Disconnect the wire from the RX1 pin. Both the Display blocks now output 0. A value of 0 in the Display Status block indicates that no data is received at the given time step. If you reconnect the wire again, you can see that the values at the Display blocks are restored.
6. To stop running the model on your hardware, click Stop on the model toolbar.
Step 5: Run the Model in Normal Mode
1. Remove the wire connecting RX1 and TX1 pins because in this model, the data is sent to a serial terminal over the Serial port 0 (USB port).
2. Open the Send Serial Data to Host Using Arduino Hardware model. This model is configured to run in Normal mode.
3. In the Configurations Parameters dialog box, go to Hardware Implementation > Target hardware resources > Groups > Serial port properties. Set Serial 0 baud rate to the maximum baud rate supported by the serial port of your Arduino hardware.
4. Double-click the Serial Transmit block and verify these parameter values.
5. On the model toolbar, set Simulation mode to Normal and click the Deploy to Hardware button. The lower left corner of the model window displays status while Simulink prepares, downloads, and runs the model on the hardware.
6. Open the serial terminal in your computer ( for example, Arduino IDE serial monitor). When logging in to the serial terminal:
Specify the COM port number that corresponds to your serial connection. To learn how to find the COM port number, see Configure Host COM Port.
Specify the baud rate to the same value as the baud rate set in the Model Configuration Parameters dialog box. In this example, the baud rate is
115200.
Garena free fire online play. After you login to the serial terminal, you can see that the counter values are displayed with label Counter_val :.
Other Things to Try
Configure Send and Receive Serial Data Using Arduino Hardware model to exchange data over other serial ports of the Arduino hardware.
Create a Simulink model that uses
Serial ReceiveandSerial Sendblocks from Instrument Control Toolbox to exchange serial data between your computer and Arduino hardware.